Proteomics data analysis software
Qlucore Omics Explorer is a next-generation bioinformatics software for research in life science, biotech, food and plant industries, as well as academia. The easy-to-use visualization-based data analysis tool with inbuilt powerful statistics delivers immediate results and provides instant exploration and visualization of multi-omics data including proteomics from a broad range of instruments.
Analyze Proteomics data
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins, particularly their expression and physical properties. Commonly quantitative methods used in proteomics are Olink®, 2D gel, LC-MS and LC-MS/MS.
The program is well suited for proteomics data analysis and lets you freely import, normalize and analyze data from proteomics experiments and generate actionable results fast and easy.
Key functionality:
- Import data from Olink ® NPX Signature and Olink® NPX Map and Olink ® Target.
- Import data from various instruments, unnormalized or normalized.
- Manage empty cells, perform prefiltering and transformations.
- Normalize data (quantile, housekeeping)
- Investigate any structure in data using variance filtering combined with PCA.
- Use the Biomarker Workbench for experiments and studies in the areas of drug development and biomarker discovery
- Generate a list of proteins that classifies data based on a selection of statistical tests: Non parametric tests, ANOVA, t-tests or regression.
- Use hierarchical clustering or PCA to identify subgroups.
- Work with Variable PCA plots to find correlation and networks among selected proteins.
- Visualize data in any of the easily configured plot types that are ready for publication.
Does it work on my data?
Answer the four quick questions below and find out if you can use Qlucore on your data.
For more details about supported data formats and data import see Data Import or Contact us with questions.
Case Studies
Analysis of proteomics data using Qlucore
The Center for Interdisciplinary Cardiovascular Sciences, Boston, USUsing proteomics to understand cardiovascular disease
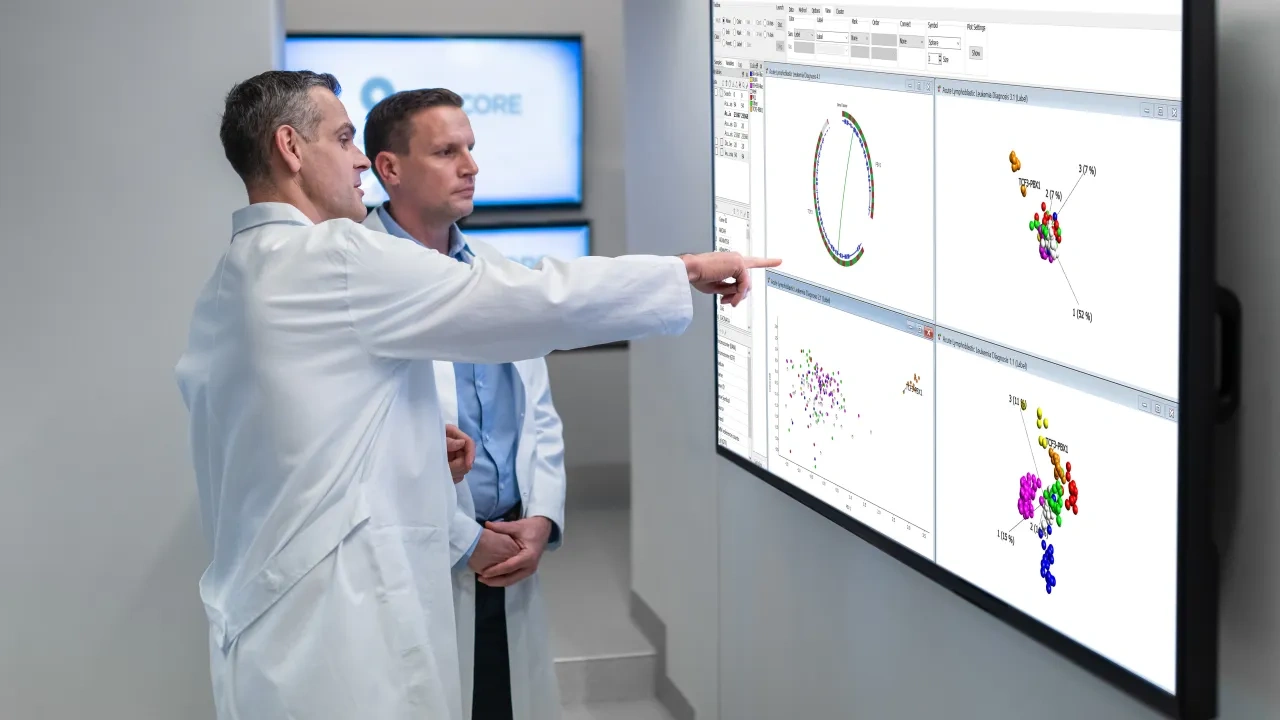
Interpreting Leukemia proteomics with Qlucore
UT MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas, USIn this case study Qlucore Omics Explorer is used to generate new ideas and hypotheses through exploration and analysis of proteomics data.
Protein data analysis in Hepatitis studies
Institute Pasteur, FranceUnderstanding viral signatures in Hepatitis C. Qlucore Omics Explorer is used to identify differences in chemokines between the virally infected groups.